This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 230/A 230M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has ben approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
- Scope
1.1 This specification covers the highest quality of round carbon steel spring wire, uniform in quality and temper, intended especially for the manufacture of valve springs and
other springs requiring high-fatigue properties.
1.2 The values stated in either SI (metric) units or inch pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; there-
fore, each system must be used independent of the other.
- Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A 370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products2
A 510 Specification for General Requirements for Wire Rods and Coarse Round Wire, Carbon Steel2
A 510M Specification for General Requirements for Wire Rods and Coarse Round Wire, Carbon Steel [Metric]2
A 700 Practices for Packaging, Marking, and Loading Methods for Steel Products for Domestic Shipment3
A 751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for Chemical Analysis of Steel Products
E 29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications4
2.2 ANSI Standard:
B 32.4M Preferred Metric Sizes for Round, Square, Rectangle, and Hexagon Metal Products
2.3 Military Standard:
MIL-STD-163 Steel Mill Products, Preparation for Shipment and Storage
2.4 Federal Standard:
FED STD No.123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
2.5 AIAG Standard:
AIAGB-5 02.00 Primary Metals Identification Tag Application Standard
- Ordering Information
3.1 Material furnished under this specification shall conform to the applicable requirements of the current edition of either Specification A 510 or A 510M.
3.2 Orders for material under this specification should include the following information for each ordered item:
3.2.1 Quantity (mass or weight),
3.2.2 Name of material (oil-tempered carbon steel valve spring quality wire),
3.2.3 Dimensions (Section 8),
3.2.4 Chemical composition (Table 1), if required,
3.2.5 Packaging (Section 14),
3.2.6 Cast or heat analysis report, if desired (see 5.2),
3.2.7 Certification or test report, or both, if specified (Section 13), and
3.2.8 ASTM designation and date of issue.
NOTE 1- -A typical metric ordering description is as follows: 20 000 kg oil-tempered carbon steel valve spring quality wire, 6.00 mm diameter in 125-kg coils to ASTM A 230M dated or for inch-pound units, 40000 lb oil-tempered carbon steel valve spring quality wire, 0.250 in. diameter in 350-1b coils to ASTM A 230 dated
- Materials and Manufacture
4.1 The steel may be made by any commercially accepted steel-making process. The steel may be either ingot cast or strand cast.
4.2 The finished wire shall be free of detrimental pipe and undue segregation.
4.3 The wire shall be hardened and tempered to produce the desired mechanical properties. 2.
- Chemical Composition
5.1 The steel shall conform to the requirements for chemical composition prescribed in Table 1.
5.2 Cast or Heat Analysis- _Each cast or heat of steel shall be analyzed by the manufacturer to determine the percentage of elements prescribed in Table 1. This analysis shall be made from a test specimen preferably taken during the pouring of the cast or heat. When requested, this shall be reported to the purchaser and shall conform to the requirements of Table 1.
5.3 Product Analysis- -An analysis may be made by the purchaser from finished wire representing each cast or heat of steel. The chemical composition thus determined, as to elements required or restricted, shall conform to the product analysis requirements specified in Table 10 of Specification A510 or A 510M.
5.4 For referee purposes, Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology A 751 shall be used.

- Mechanical Properties
6.1 Tension Test:
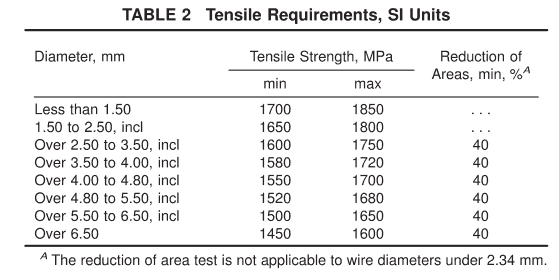
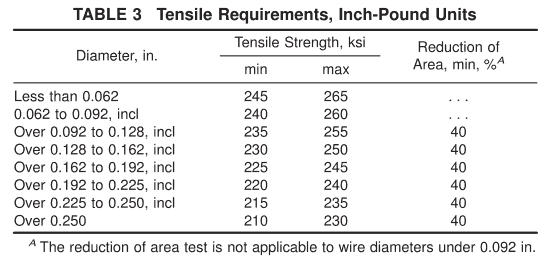
6.1.1 Requirements- -The material as represented by tension test specimens shall conform to the requirements prescribed in Table 2 or Table 3.
6.1.2 Number of Tests- _One test specimen shall be taken for each five coils, or fraction thereof, in a lot. Each cast or heat in a given lot shall be tested.
6.1.3 Location of Tests- -Test specimens shall be taken from either end of the coil.
6.1.4 Test Method- The tension test shall be made in accordance with Test Methods and Definitions A 370.
6.2 Wrap Test:
6.2.1 Requirements- _Wire 4.00 mm or 0.162 in. and smaller in diameter shall wind on itself as an arbor without breakage. Larger diameter wire, up to and including 6.50 mm or 0.250 in, shall wind, without breakage, on a mandrel twice the diameter of the wire.
6.2.2 Number of Tests- _One test specimen shall be taken for each five coils, or fraction thereof, in a lot. Each cast or heat in a given lot shall be tested.
6.2.3 Location of Test- -Test specimens shall be taken from either end of the coil.
6.2.4 Test Method- -The wrap test shall be made in accordance with Test Methods and Definitions A 370, Supplement IV.
6.3 Twist Test- -A 250 mm (10 in.) specimen of wire slowly twisted four revolutions in one direction and then twisted in the other direction until failure shall show a square break normal to the axis of the wire without splits or cracks.
6.4 Special Surface Inspection- When specified, the entire length of every coil used by engine valve spring manufacturers shall be inspected for surface imperfections with a magnetic and/or eddy current defect analyzer or equivalent.
- Metallurgical Properties
7.1 Decarburization:
7.1.1 Requirements- -Transverse sections of the wire properly mounted, polished and etched shall show no completely decarburized (carbon free) areas when examined at 100X magnification. Partial decarburization shall not exceed a depth of 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) on wire 4.90 mm (0.192 in.) and smaller or 0.038 mm (0.0015 in.) on wire larger than 4 90 mm (0.192 in.). Measure the worst area present excluding decarburization associated with seams or other surface imperfections. Complete decarburization exists when only free ferrite is present. Partial decarburization exists when ferrite is found mixed with pearlite or tempered martensite. Structures of 100 % tempered martensite shall be defined as not decarburized.
7.1.2 Number of Tests- _One test specimen shall be taken for each five coils, or fraction thereof, in a lot.
7.1.3 Location of Tests- -Test specimens may be taken from either end of the coil.
7.2 Surface Condition:
7.2.1 The surface shall be smooth and free of defects such as seams, pits, die marks, and other defects tending to impair the fatigue value of the springs. Any additional surface requirements must be negotiated at the time of entry of the order.
7.2.2 Number of Tests- One test specimen from each end of every coil shall be tested for conformance to the provisions of 7.2.1.
7.2.3 Test Method- -The surface shall be examined after etching in a solution of equal parts of hydrochloric acid and water that has been heated to approximately 80°C for a
sufficient length of time to remove up to approximately 1 % of the diameter of the wire. Examination shall be made using 10X magnification.
7.3 Microstructure- _A longitudinal section shall show a fine homogeneous tempered martensitic structure.
- Dimensions and Permissible Variations
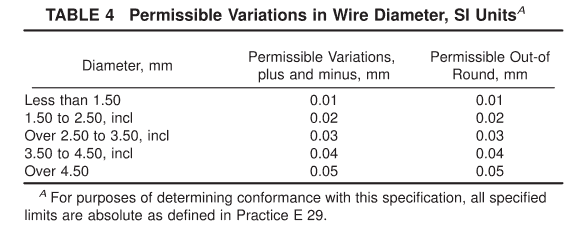
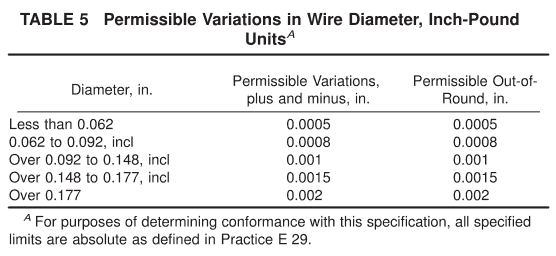
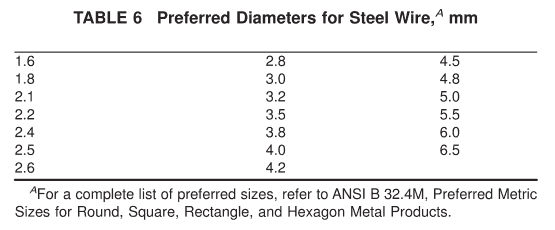
8.1 The permissible variations in the diameter of the wire shall be as specified in Table 4 or Table 5. The preferred wire diameters are listed in Table 6.
8.2 Number of Tests- One test specimen from each end of the coil shall be tested for conformance (see 8.1).
- Workmanship and A ppearance
9.1 The wire shall be uniform in quality and temper and shall not be wavy or crooked.
9.2 Each coil shall be one continuous length of wire, properly coiled, and firmly tied.
9.3 No welds are permitted in the finished product and any welds made during processing must be removed.
- Retests
10.1 If any test specimen exhibits obvious defects or shows the presence of a weld, it may be discarded and another specimen substituted.
- Inspection
11.1 Unless otherwise specified in the contract or purchase order, the manufacturer is responsible for the performance of all inspection and test requirements specified in this specification. Except as otherwise specified in the contract or purchase order, the manufacturer may use his own or any other suitable facilities for the performance of the inspection and test requirements unless disapproved by the purchaser at the time the order is placed. The purchaser shall have the right to perform any of the inspections and tests set forth in this specification when such inspections and tests are deemed necessary to assure that the material conforms to prescribed requirements.
- Rejection and Rehearing
12.1 Unless otherwise specified, any rejection based on tests made in accordance with this specification shall be reported to the manufacturer as soon as possible so that an investigation may be initiated.
12.2 The material must be adequately protected and correctly identified in order that the manufacturer may make a proper investigation.
- Certification
13.1 When specified in the purchase order or contract, a manufacturer’s or supplier’ s certification shall be furnished to the purchaser that the material was manufactured, sampled, tested, and inspected in accordance with this specification and has been found to meet the requirements. When specified in the purchase order or contract, a report of the test results shall be furnished.
13.2 The certification shall include the specification number, year date of issue, and revision letter, if any.
- Packaging, Marking, and Loading for Shipment
14.1 The coil mass, dimensions, and the method of packaging shall be as agreed upon between the manufacturer and purchaser.
14.2 The size of the wire, purchaser’ s order number, ASTM specification number, heat number, and name or mark of the manufacturer shall be marked on a tag securely attached to each coil of wire.
14.3 Unless otherwise specified in the purchaser’s order, packaging, marking, and loading for shipments shall be in accordance with those procedures recommended by Practices A 700.
14.4 For Government Procurement- -Packaging, packing, and marking of material for military procurement shall be in accordance with the requirements of MIL -STD-163, Level A, Level C, or commercial as specifed in the contract or purchase order. Marking for shipment of material for civil agencies shall be in accordance with Fed. Std. No. 123.
14.5 Bar Coding- -In addition to the previously-stated identification requirements, bar coding is acceptable as a supplementary identification method. Bar coding should be consistent with AIAG B-5 02.00, Primary Metals Identification Tag Application. The bar code may be applied to a substantially affixed tag.
- Keywords
15.1 carbon; oil-tempered; valve spring; wire