1 Scope
This part of ISO 8458 specifies requirements for oil-hardened and tempered carbon and low alloy steel wire, for the manufacture of mechanical springs for static duty and dynamic duty applications, complying with the general requirements of ISO 8458-1.
2 Normative references
The following normative documents contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of this part of ISO 8458. For dated references, subsequent amendments to, or revisions of, any of these publications do not apply. However, parties to agreements based on this part of ISO 8458 are encouraged to investigate the possibility of applying the most recent editions of the normative documents indicated below. For undated references, the latest edition of the normative document referred to applies. Members of ISo and IEC maintain registers of currently valid International Standards.
ISO 4967:1998,Steel- Determination of content of non-metallic inclusions 一Micrographic method using standard diagrams ISO 8458-1, Steel wire for mechanical springs一Part 1: General requirements
3 Classification and designation
The various spring wire grades and the relevant diameters are shown in Table 1.
Table 1一Spring wire grades and diameter ranges
| Tensile Strength | Static | Medium fatigue | High fatigue |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low tensile strength | FDC | TDC | VDC |
| Medium tensile strength | FDCrV(A.B) | FDCrV(A.B) | VDCrV(A.B) |
| High tensile strength | FDSiCr | TDSiCr | VDSiCr |
| Diameter range (mm) | 0.50 to 17.00 | 0.50 to 10.00 | 0.50 to 10.00 |
FD grade is intended for static applications, required for normal springs.
TD grade is intended for medium fatigue levels.
VD grade is intended for use under severe dynamic duty such as for valve springs.
4 Dimensional tolerances
The permissible dimensional tolerances on wire in coils and cut lengths shall be in accordance with those specified in ISO 8458-1. When the required tolerance level is different from those mentioned above, it shall be agreed at the time of ordering.
5 Requirements
5.1 Chemical composition
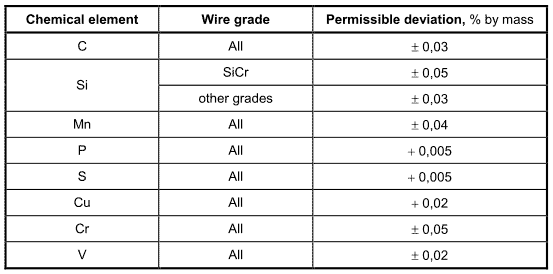
The steel is characterized by the heat analysis, which shall be in accordance with the values listed in Table 2. The permissible deviation of the product analysis from the heat analysis shall be in accordance with Table 3.
Table 2 – – Chemical composition, mass fraction
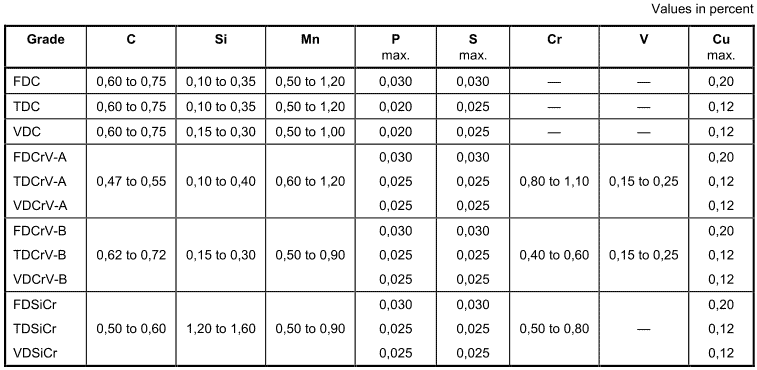
Table 3- Permissible deviation of the product analysis from the limiting values for the heat analysis
5.2 Surface quality
5.2.1
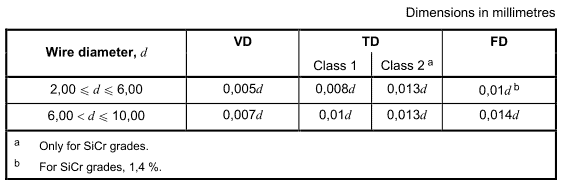
The surface of the wire shall be smooth. The permissible maximum depth of surface discontinuities measured on samples as defined in ISO 8458-1 shall be in accordance with Table 4.
Table 4一Permissible maximum depth of surface discontinuities
5.2.2 Eddy current inline testing shall be performed for VD grades and is optional for TD grades. The method of testing and the evaluation of test results shall be agreed upon between the parties. Eddy current testing is normally applied for sizes 2,50 mm to 6,00 mm.
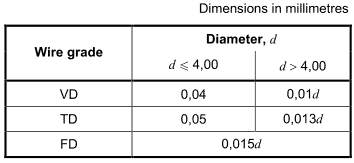
5.2.3 The cross-section of ire of VD and TD shall be free from complete decarburization. The permissible maximum average depths of partial decarburized layer are shown in Table 5.
Table 5一- Permissible maximum average depth of surface decarburization
5.3 Non-metallic inclusions
The VD grades shall be checked for maximum size of inclusion in accordance with ISO 4967. The permissible level of inclusions shall be agreed upon between the parties at the inquiry and order.
5.4 Mechanical properties
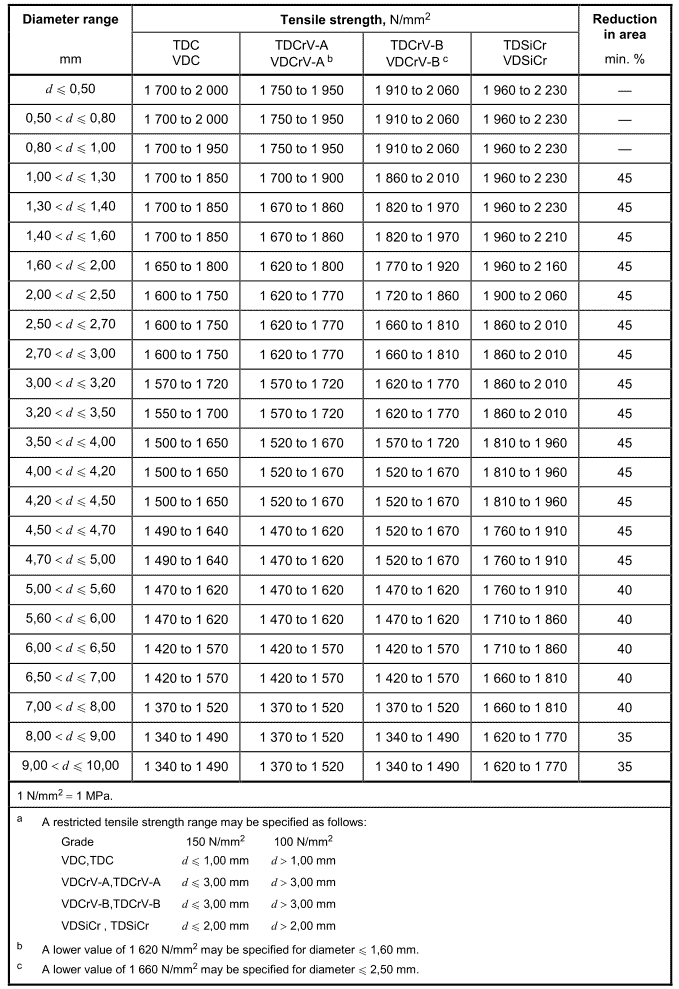
For tensile strength and reduction in area after rupture, the wire grades shall satisfy the values listed in Table 6 and Table 7. Reduction of area shall be measured only for sizes 1,00 mm and above. The range of tensile strength values within a coil/reel shall not exceed 50 N/mm2 for the grades VD, 60 N/mm2 for the grades TD and 70 N/mm2 for the grades FD.
5.5 Technological properties
5.5.1 Wrapping test
5.5.1.1 The wrapping test may be applied to wires with nominal diameter less than 3,00 mm.
5.5.1.2 The wire shall not show any sign of fracture when closely coiled for at least four turns around a mandrel of diameter equal to that of the wire.
Table 6一Mechanical properties for oil-hardened and tempered spring steel wire of static duty
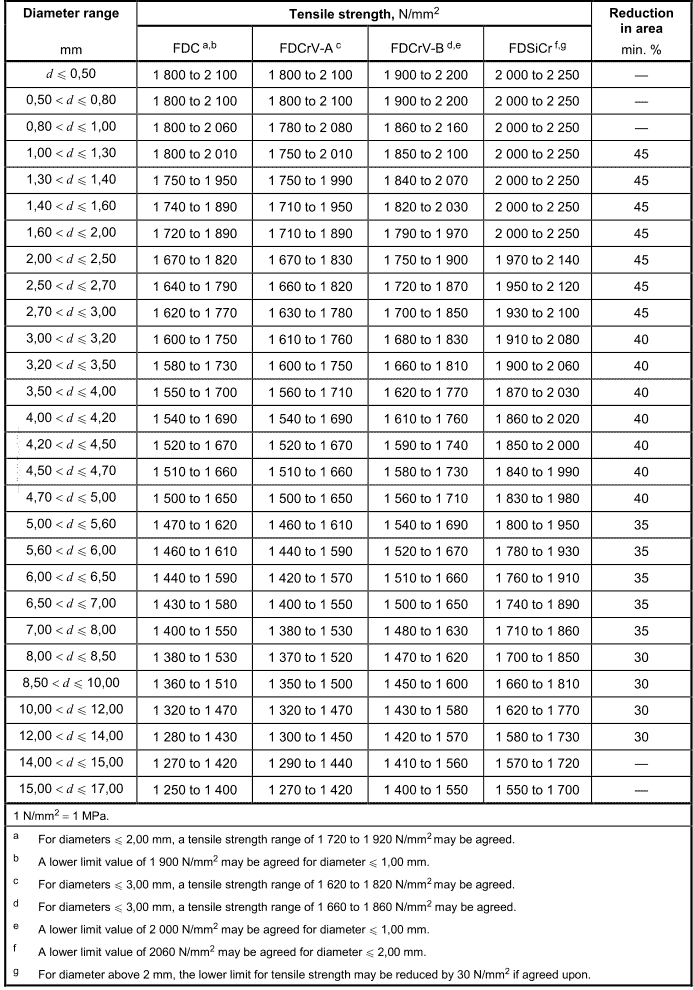
Table 7 – Mechanical properties for oil-hardened and tempered spring steel wire of dynamic duty
5.5.2 Torsion test
5.5.2.1 The torsion test shall be applied to wires of nominal diameters from 0,70 mm to 6,00 mm, using a gauge length equivalent to 100 wire diameters. Other gauge lengths are permitted only by agreement.
5.5.2.2 There are two methods for the torsion test. In the first method the torsion test piece shall be twisted in one direction until fracture. No harmful defects shall be visible on surface after fracture. The fracture plane shall be perpendicular to the wire axis and show no visible cracks. The minimum number of torsions required may be specified at the time of ordering.
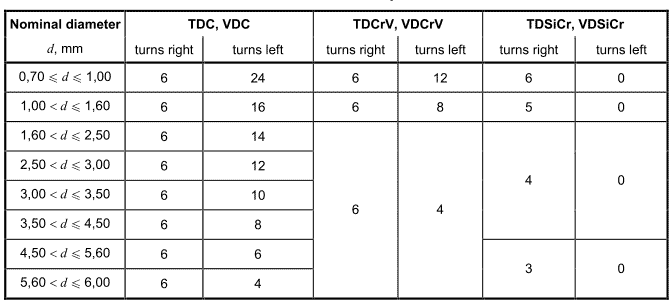
The second method, in which the torsion test piece shall be twisted in two directions, is optional for grade TD and VD. The requirements specified in Table 8 shall be applied.
Table 8一Torsion test requirements
5.5.3 Bend test
5.5.3.1 The bend test may be applied to wires with nominal diameter greater than 6,00 mm.
5.5.3.2 The wire shall not show any sign of fracture when bent through an angle of 90° around a mandrel of diameter equal to twice the wire diameter.
5.5.4 Coiling test
The coiling test may be applied to wires with nominal diameter not more than 0,70 mm.
6 Test methods and other requirements
Test methods and general requirements shall be in accordance with ISO 8458-1. For details, see Table 9.
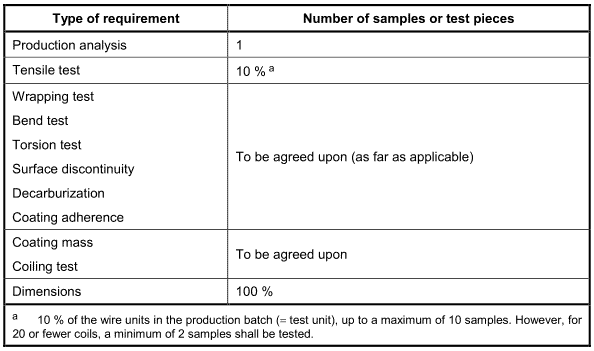
The extent of testing shall be in accordance with Table 10.
Table 9 – Summary of the information on test methods and requirements
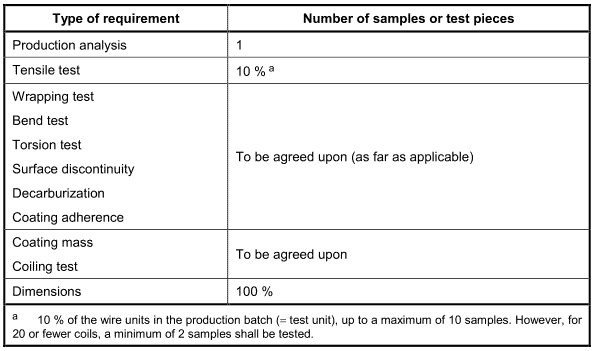
Table 10一Acceptance unit and number of samples and test pieces