This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 313/A 313M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers austenitic and age-hardenable stainless steel round spring wire intended especially for the manufacture of springs.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as the standard. Within the text and tables, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification.
1.3 Unless the order specifies an “M” designation, the material shall be furnished to inch-pound units.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A 555/A 555M Specification for General Requirements for Stainless Steel Wire and Wire Rods
A 751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for Chemical Analysis of Steel Products
E 527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS)
2.2 Society of Automotive Engineers Standard:
J 1086 Numbering Metals and Alloys
3. Ordering Information
3.1 It is the responsibility of the purchaser to specify all requirements that are necessary for material ordered under this specification. Such requirements may include, but are not limited to the following:
3.1.1 Quantity (weight),
3.1.2 Name of material (stainless steel spring wire),
3.1.3 Finish (see 8.1),
3.1.4 Dimension (diameter),
3.1.5 Type designation (Table 1),
3.1.6 ASTM designation and date of issue,
3.1.7 Supplementary requirements for government procurement, and
3.1.8 Special requirements.
NOTE 1—A typical ordering description is as follows: 2000 lb (1000 kg) Stainless Steel Spring Wire, cold-drawn Class 1, bright finish, 0.032-in. (0.82 mm) diameter, in 100-lb (50 kg) 16-in. (0.4 m) coils, Type 302 to ASTM A 313, dated ____.
4. General Requirements for Delivery
4.1 In addition to the requirements of this specification, all requirements of the current edition of Specification A 555/A 555M shall apply. Failure to comply with the general requirements of Specification A 555/A 555M constitutes nonconformance with this specification.
5. Manufacture
5.1 Types 302 Class 1, 304, 305, 316, 321, 347, and Grades S20430 and XM-28 shall be cold drawn to produce the required mechanical properties.
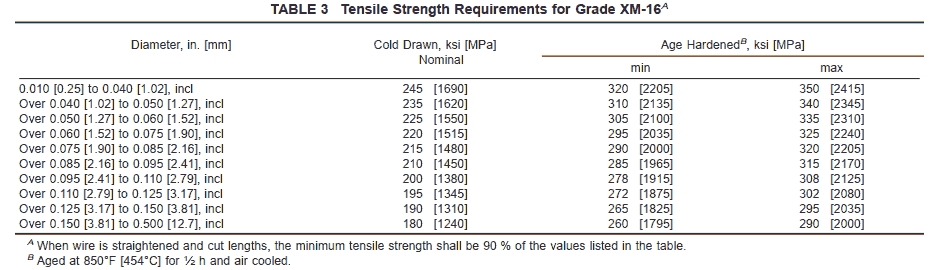
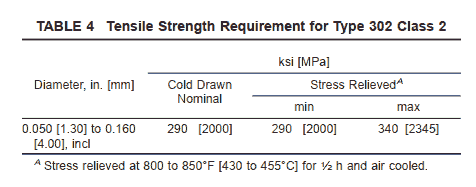
5.2 Type 631, Type 302 Class 2, and Grade XM-16 shall be furnished in the cold-drawn condition ready for fabrication. Following fabrication Type 631 and Grade XM-16 shall be age or precipitation hardened to produce their maximum strength properties. The tensile strengths to be obtained following the prescribed heat treatment are shown in Table 2 and Table 3 for hardened wire. Type 302 Class 2 shall be stress relieved following fabrication and meet the requirements shown in Table 4. The nominal as-drawn tensile strengths are provided as a guide for the spring manufacturer.
6. Chemical Composition
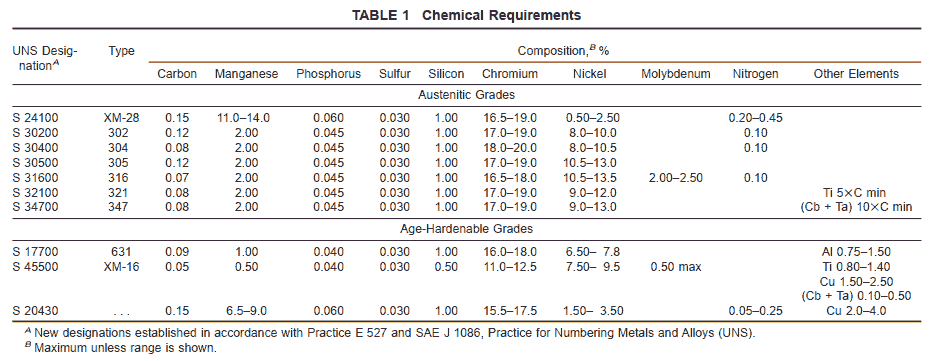
6.1 The steel shall conform to the requirements as to chemical composition prescribed in Table 1.
6.2 Methods and practices relating to chemical analysis required by this specification shall be in accordance with Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology A 751
7. Mechanical Requirements
7.1 Tensile Properties:
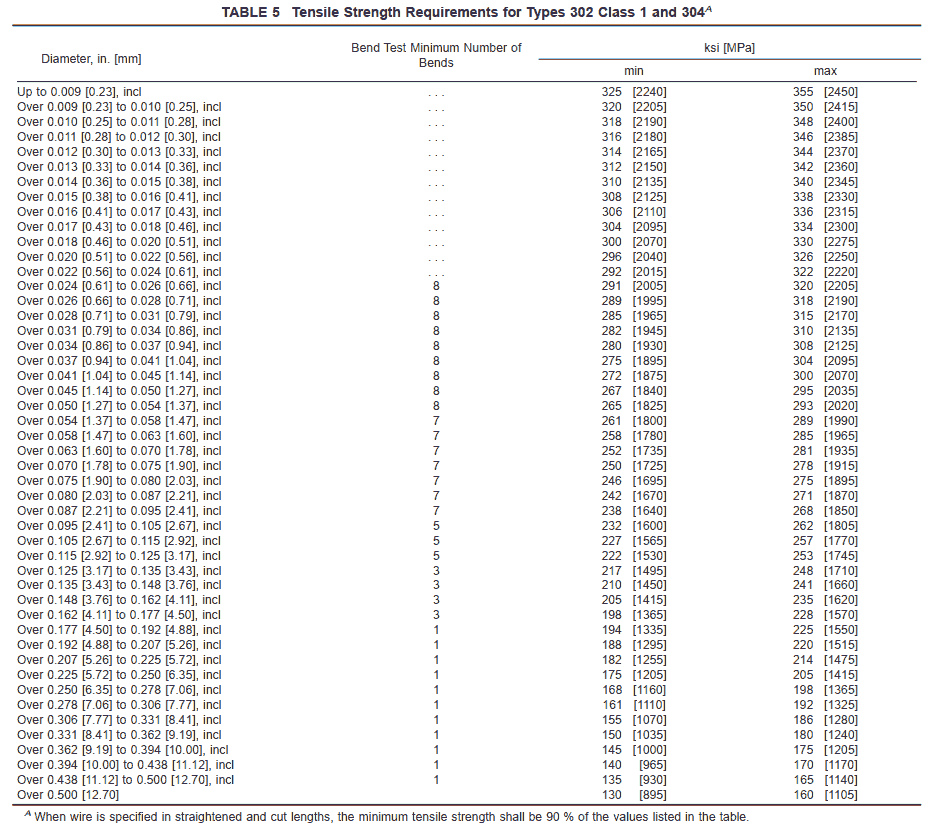
7.1.1 Types 302 Class 1 and 304 shall conform to the requirements shown in Table 5.
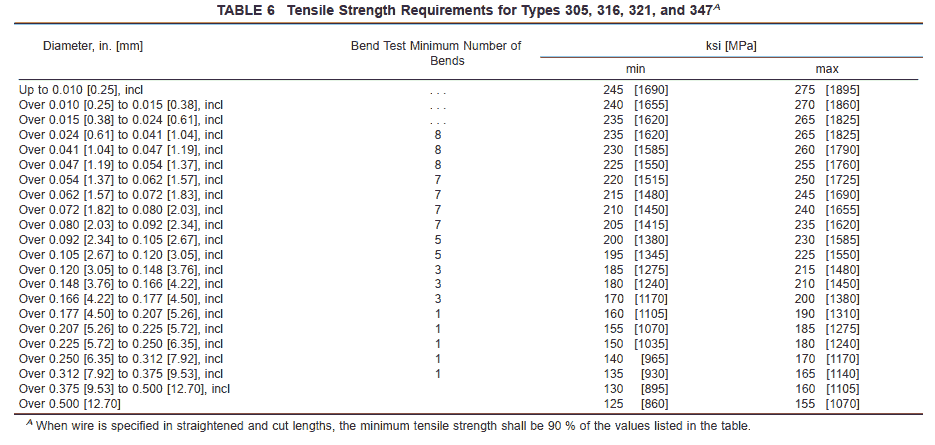
7.1.2 Types 305, 316, 321, and 347 shall conform to the requirements shown in Table 6.
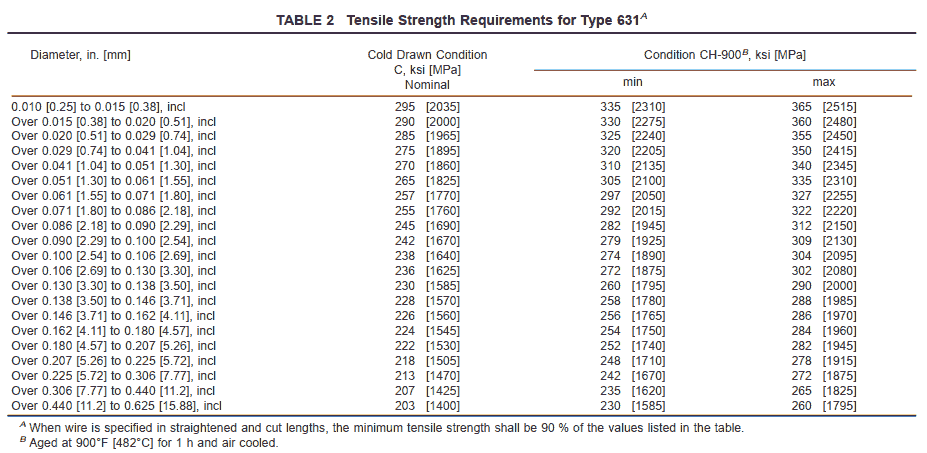
7.1.3 Type 631 shall conform to the requirements shown in Table 2 when heat treated 900°F [482°C] for 1 h and air cooled.
7.1.4 Grade XM-16 shall conform to the requirements shown in Table 3 when heat treated 850°F [454°C] for 1⁄2 h and air cooled.
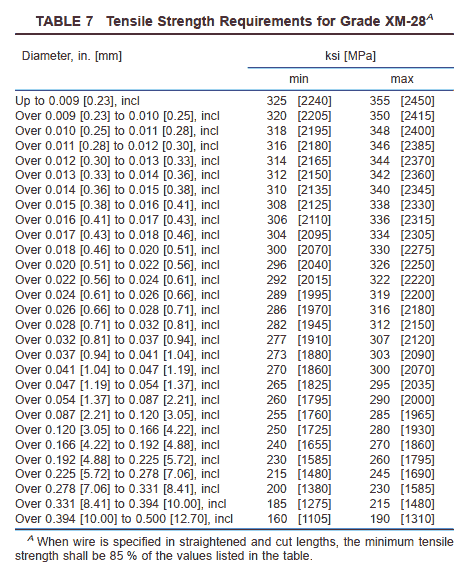
7.1.5 Grade XM-28 shall conform to the requirements shown in Table 7.
7.1.6 Type 302 Class 2 shall conform to the requirements shown in Table 4.
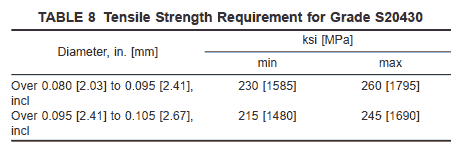
7.1.7 Grade S20430 shall conform to the requirements shown in Table 8.
7.2 Wrap Test:
7.2.1 Wire 0.162 in. [4.11 mm] and smaller in diameter shall wind on itself as an arbor without breaking.
7.2.2 Wire larger than 0.162 in. [4.11 mm] in diameter shall wind without breaking on a mandrel having a diameter twice the diameter of the wire.
7.3 Uniformity (Coil Test):
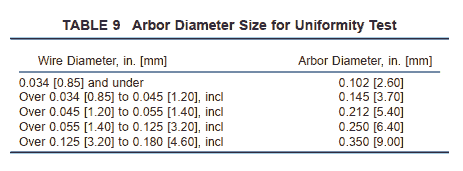
7.3.1 In the as-cold drawn condition, a specimen coil shall be wound on an arbor of the size specified in Table 9 to form a tightly wound coil.
7.3.2 After winding, the specimen coil shall be stretched to a permanent set four times its as-wound length. After this treatment, the specimen coil shall show uniform pitch with no splits or fractures.
7.4 Cast—A loop or ring shall be cut from the bundle and allowed to fall on the floor. The wire shall lie flat and not spring up or show a wavy condition.
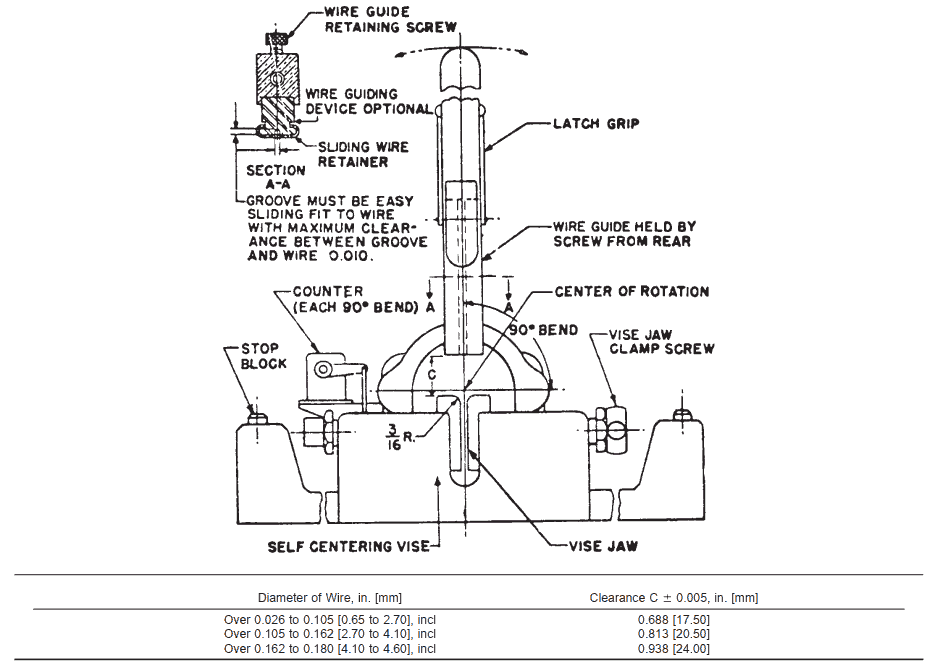
7.5 Bend Test—When specified in the purchase order, Types 302, 304, 305, 316, 321, and 347 shall be tested by the bend test. A piece not more than 10 in. [254 mm] long shall be selected from each test sample. These specimens shall be tested in a bending machine conforming substantially to Fig. 1. Bends shall be made at as nearly a uniform rate as possible, not exceeding 50 bends per minute, and in no case shall the speed be so great as to cause undue heating of the wire. The test specimen shall be bent back and forth through a total angle of 180° until failure occurs. Each 90° movement in either direction shall be counted as one bend. The wire shall withstand the minimum number of bends specified in Table 5 and Table 6.
8. Finish
8.1 Stainless steel spring wire is supplied with different
types of finish such as bright, copper, lead, oxide, and other.
9. Keywords
9.1 austenitic stainless steel; precipitation hardening stainless steel; stainless steel spring wire